Specification
- फ़्रिक्वेंसी
- हर्ट्ज (एचजेड)
- टाइप करें
- Soft Drink Machinery
- मटेरियल
- Mild Steel
- कम्प्यूटरीकृत
- स्वचालित ग्रेड
- वोल्टेज
- वोल्ट (v)
- रंग
- Silver
- वारंटी
- 1 Year
- सतह की फ़िनिश
Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Unit
- भुगतान की शर्तें
- , ,
- डिलीवरी का समय
- दिन
- मुख्य निर्यात बाजार
- , , , , , , , ,
About
Soft Drink Plant is a facility designed to produce, bottle (or can), package, and distribute beveragestypically non-alcoholic and often carbonatedon a commercial scale. The plant integrates several interconnected stages involving raw material processing, flavor production, carbonation, filling, quality control, packaging and logistics.
Key Components & Process Flow
-
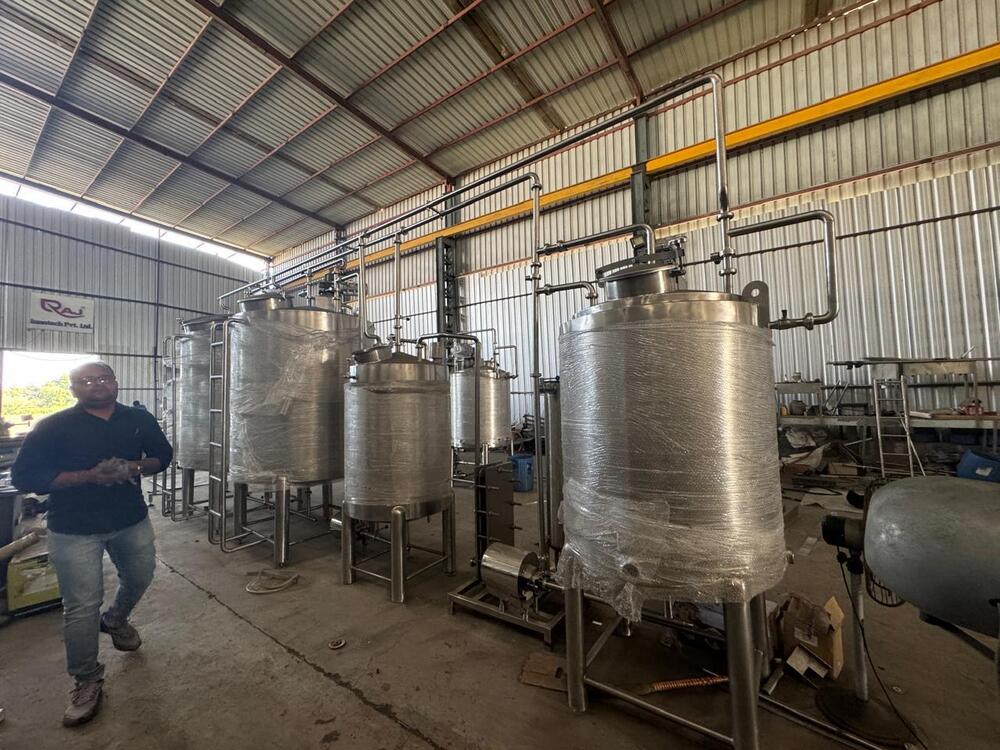
Raw Material Treatment
-
Water Treatment: Purification (filtration, reverse osmosis, UV or chemical disinfection) to ensure water meets purity standards.
-
Syrup/Flavor Preparation: The flavor concentrates, sweeteners, colors, preservatives etc., are prepared and blended as per product formulations.
-
-
Carbonation / Mixing
-
Carbon dioxide (CO) is infused into treated water in controlled conditions to get desired effervescence (for carbonated soft drinks).
-
Mixing systems ensure uniform blending of water, syrup, flavors, and carbon dioxide.
-
-
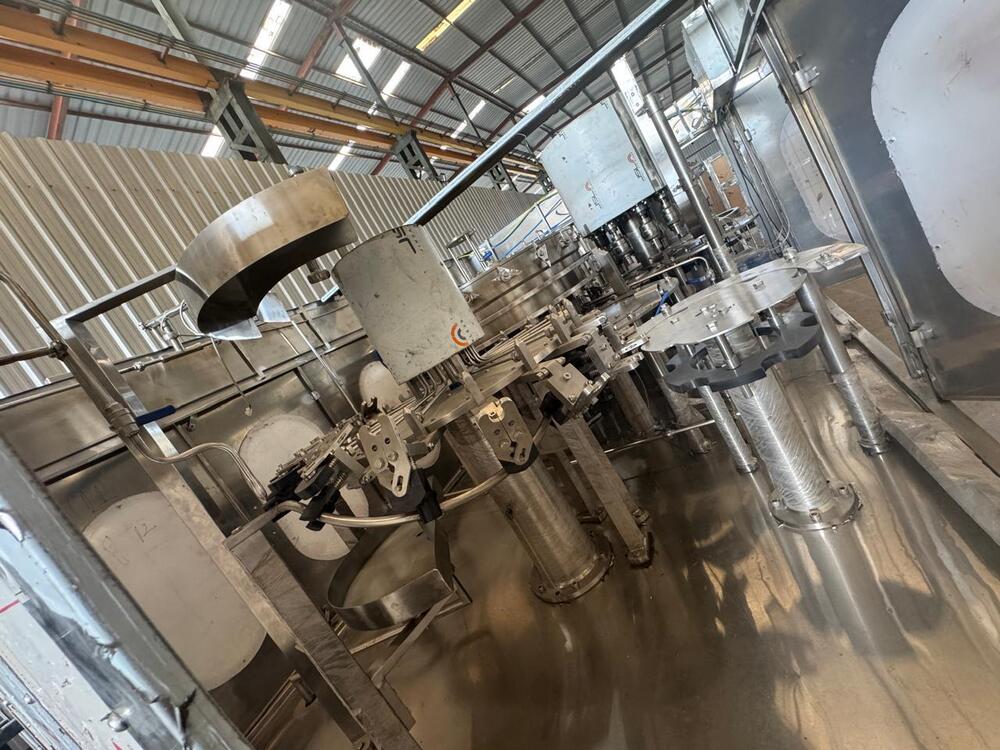
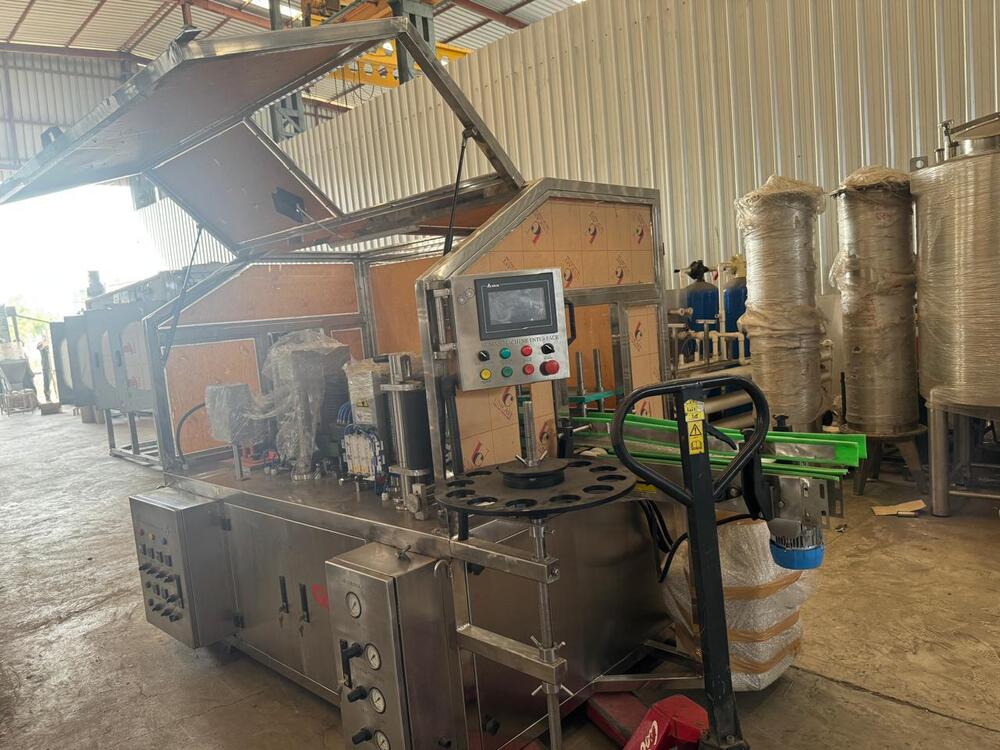
Filling, Capping, Sealing
-
Bottles/cans are rinsed/sanitized, filled, and sealed under hygienic & automated conditions.
-
Equipment includes filling machines, capping or sealing units, often with automation to reduce contamination risk.
-
-
Packaging
-
After sealing, packaging (labeling, shrink wrapping, corrugated cartons etc.) is done to make the product ready for transport.
-
Emphasis on branding, protection (against light, air), and ensuring shelf stability.
-
-
Quality Control & Safety
-
QC at all stages: water quality, syrup mix accuracy, carbonation level, fill volume, microbiological safety, packaging integrity.
-
Use of sensors, PLC controls, CIP (Clean In Place) systems, automated monitoring of key parameters (temperature, pressure etc.).
-
-
Automation & Utilities
-
Many modern soft drink plants are fully or partially automated (PLC/SCADA systems) to improve efficiency, consistency, and reduce labor.
-
Utilities: electricity, boiler/steam, refrigeration/chillers, compressed air, CO supply, waste water treatment.
-
-
Logistics & Distribution
-
Finished products are warehoused, palletized, then dispatched via trucks (or via distributors) to covering wholesalers, retailers, vending points etc.
-
Cold chain may be required depending on type of drink and local climate.
-
Features & Benefits
-
High Throughput: Designed to produce large volumes (e.g. tens to hundreds of bottles per minute) to meet commercial demand.
-
Consistency & Quality: Automation and strict QC ensure each batch matches flavor, carbonation, appearance, and safety norms.
-
Hygiene & Safety: Use of food-grade stainless steel, sanitization/CIP, sealed environments to prevent contamination.
-
Cost Efficiency: Better material utilization (less wastage), energy efficiency, reduced labor through automation.
-
Scalability & Flexibility: Ability to change bottle sizes, flavors, or packaging formats with modular equipment.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to food safety regulations (FSSAI in India, or equivalent), environmental rules (waste water, CO emissions etc.).
Robust Construction and Design
Crafted from high-grade mild steel with a polished silver surface, our machinery combines durability with aesthetic appeal. The semi-automatic mechanism ensures straightforward operation while minimizing manual intervention, ideal for scaling up production in industrial environments.
Reliable Performance Across Industries
This soft drink machinery is built to function effectively at a frequency of 50 Hertz, with adaptable voltage capabilities. Its design caters to businesses of varying scales, from wholesalers to exporters, making it a versatile choice for beverage production throughout India.
FAQs of Soft Drink Machinery:
Q: How does the semi-automatic soft drink machinery operate?
A: The semi-automatic operation involves manual input for certain steps such as loading ingredients, while automated systems handle mixing and filling. This approach streamlines production without complete reliance on complex computer controls.Q: What are the advantages of choosing mild steel as the material for this machinery?
A: Mild steel offers excellent strength and corrosion resistance, making the equipment durable and able to withstand continuous use in demanding manufacturing environments.Q: When is the optimal time to schedule routine maintenance for this soft drink machinery?
A: Routine maintenance is recommended every three to six months to ensure peak performance and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Regular servicing also supports the longevity of the one-year warranty.Q: Where can this soft drink machinery be installed?
A: The machinery is suitable for installation in factories, beverage production units, and commercial bottling facilities across India, thanks to its adaptable voltage range and robust construction.Q: What is the process involved in producing soft drinks using this machine?
A: The typical process includes loading ingredients, mixing them, and dispensing the mixture into containers. The machine automates critical tasks while allowing user supervision for quality assurance.Q: How can using this machinery benefit beverage manufacturers and suppliers?
A: Utilizing this machinery enhances production efficiency, ensures consistent product quality, and reduces labor costs by automating key steps in the soft drink manufacturing process.Q: What warranty protection is provided with the soft drink machinery?
A: Each unit comes with a one-year warranty covering manufacturing defects, ensuring reliable support and peace of mind for buyers.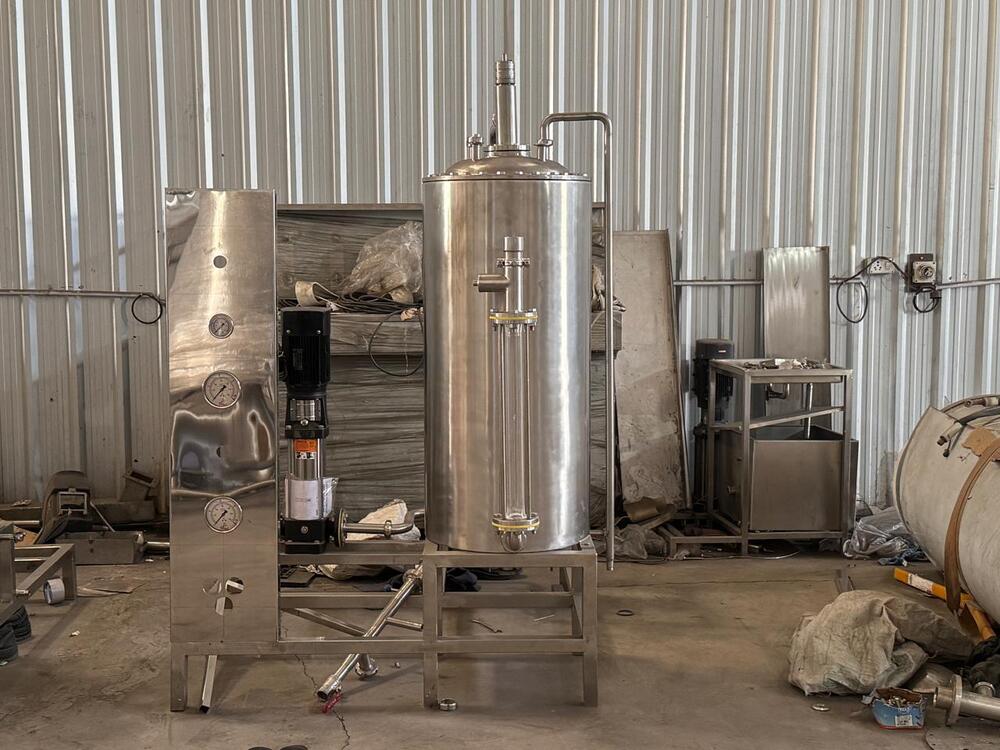




Price: Â
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+




 जांच भेजें
जांच भेजें एसएमएस भेजें
एसएमएस भेजें मुझे निःशुल्क कॉल करें
मुझे निःशुल्क कॉल करें English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese